 The documented risks of these drugs are provided so the public can make informed, educated decisions. Ativan is a benzodiazepine (antianxiety drug). The FDA cites suicidal ideation/attempts are side side effects of Ativan. The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration warns that benzodiazepines can bring about hostility, as well as physical dependence. Ativan is also known as Idalprem, Lorax, Lorazepam, Orfidal, Tavor, Temesta, Wypax.
The documented risks of these drugs are provided so the public can make informed, educated decisions. Ativan is a benzodiazepine (antianxiety drug). The FDA cites suicidal ideation/attempts are side side effects of Ativan. The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration warns that benzodiazepines can bring about hostility, as well as physical dependence. Ativan is also known as Idalprem, Lorax, Lorazepam, Orfidal, Tavor, Temesta, Wypax.
To see the total figures from IQVia on the number of people taking antianxiety drugs in the U.S., click here.
Please note: No one should attempt to get off of psychiatric drugs without a doctor’s supervision. To help find medical practitioners in your area, click here.
Also, read the FDA’s Ativan Medication Guide for more information. MedGuides include “the particular serious and significant public health concern that has created the need for the Medication Guide” and notes “pediatric risks.” (Note: Unfortunately, the FDA MedGuides only work on a desktop, not on a mobile device. Please complain to the FDA to make their public advisories accessible to all. 1-888-INFO-FDA or 1-888-463-6332.)
Drug Warnings:
There has been one drug regulatory agency warning from the United States warning that Ativan can cause profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma and death when used in combination with opioids.
Drug Studies:
There have been five studies done in three countries (Canada, United Kingdom and United States) on Ativan (or lorazepam). These include the following (note that some studies cite more than one side effect, so the list below may not be equal to the total number of studies):
2 studies on Ativan causing dementia
1 study on Ativan causing death or increased risk of death
1 study on Ativan causing risk of fractures
1 study on Ativan causing impaired driving or sleep-driving
1 study on Ativan causing cognitive impairment
1 study on Ativan causing sedation
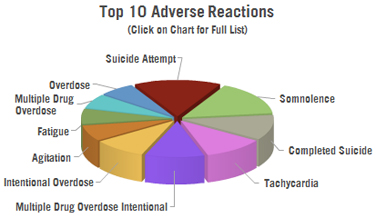
Adverse Reaction Reports Filed with the US FDA: There have been 2,727 adverse reactions reported to the US FDA in connection with Ativan.
The FDA estimates that less than 1% of all serious events are ever reported to it, so the actual number of side effects occurring are most certainly higher.
- 329 cases of suicide attempt
- 325 cases of somnolence
- 239 cases of completed suicide
- 230 cases of tachycardia (rapid heart rate)
- 224 cases of multiple drug overdose, intentional
- 201 cases of intentional overdose
- 151 cases of agitation
- 148 cases of fatigue
- 138 cases of multiple drug overdose
- 135 cases of overdose
Documented Side Effects of Ativan:
Source: Physicians Desk Reference, National Institutes of Health’s Medline Plus, and/or the drug label.
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the heart cavity
Abnormal physical weakness or lack of energy
Abnormally slow heart action
Agitation
Amnesia
Anxiety
Apnea
Blurred vision
Buildup of lactic acid in the body
Cardiac arrest
Chills
Coma
Confusion
Congenital malformations
Constipation
Deficiency of white blood cells
Deficiency in amount of oxygen reaching body tissues
Deficiency of all three cellular components of the blood (red cells, white cells, and platelets)
Delirium
Depression
Diarrhea
Dizziness
Double vision
Drowsiness
Elevated liver enzymes
Euphoria
Excess fluid in the lungs
Excessive quantities of acid in the body or kidneys not removing enough acid from the body
Fatigue
Gastrointestinal bleeding
Hair loss
Hallucinations
Headache
Hearing loss
Heart failure
Hostility
Hyperactivity
Hypersalivation
Hypertension
Hyperventilation
Hypotension
Hypothermia
Hypoventilation
Impairment in blood’s ability to form clots
Impotence
Inflammation of the urinary bladder
Injection site reaction
Insomnia
Irregular involuntary contraction of muscles
Irritability
Jaundice
Libido decrease
Libido increase
Life-threatening allergic reaction
Loss of full control of bodily movements
Low sodium level in the blood
Mania
Memory impairment
Muscle paralysis
Nausea
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Nightmares
Orgasm dysfunction
Overactive or overresponsive reflexes
Physiological dependence
Presence of air or gas in the cavity between the lungs and the chest wall, causing collapse of the lung
Psychological dependence
Psychosis
Pulmonary hypertension
Rash
Respiratory arrest
Respiratory depression
Restlessness
Seizures
Slurred speech
Suicidal ideation/attempts
Superficial reddening of the skin, usually in patches
Sweating, especially to an unusual degree
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion
Tremor
Urinary incontinence
Vertigo
Vomiting
Weakness
Withdrawal
Click here to learn more >>
This brochure is a simple guide that documents the dangerous and deadly side effects of the drugs prescribed to millions of men, women and children diagnosed with bogus mental disorders.


 Download The Side Effects of Common
Download The Side Effects of Common
SHARE YOUR STORY/COMMENT